Nginx
About
Nginx (pronounced engine-x) is web server which can also be used proxy, load balancer, mail proxy and HTTP cache. It's also a modern alternative to something like Apache, IIS, or Caddy.
Prerequisites
An nginx installation should be pretty accessible regardless of your OS. This guide is specifically written for Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS, but should work on any other type of Unix operating system. The setup that we're using is commonly referred to as a LEMP stack (Linux, nginx, MySQL, PHP.)
- nginx/1.14.0 (Ubuntu)
- PHP 7.2.10-0ubuntu0.18.04.1 (cli)
- MySQL v14.14 Distribution 5.7.24
If you've just installed a new operating system, you'll want to update your local package index by running sudo apt-get update, and then add the Universe repository by running sudo apt-add-repository universe.
Installing nginx
To start, you're going to want to install nginx using the aptitude package manager. You can do this by running sudo apt-get install nginx. Once you run that, you'll want to go through the configuration prompt that appears.
.
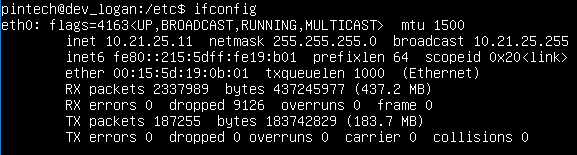
After nginx and its subsequent dependencies have finished installing, you'll want to let it through the firewall by running sudo ufw allow 'Nginx HTTP'. Check what your current IP is by running ifconfig, and then look for whatever interface looks correct. In this instance, the proper interface is eth0.
.
After running the command, the first indented line should say inet and then an IP address afterwards. Verify functionality of nginx by going to your web browser and typing http://{ip}/ where {ip} is what follows after inet.
If the default nginx page displays, continue to the next section.
.
.
.
.
.
Installing MySQL
The process of installing MySQL is fairly similar to installing nginx, although MySQL does require a little bit of configuration before it will function properly. Start off by running sudo apt-get install mysql-server, and then once it finishes run the setup script by typing sudo mysql_secure_installation.
.
The first thing that the installations script will ask you is if you'd like to enable the VALIDATE PASSWORD PLUGIN, but don't. If you don't care about why, then skip to the next paragraph, but if you do, keep reading. Essentially, the plugin throws errors if passwords don't meet specific criteria. This causes issues if you either a.) use weak passwords, or b.) install a package that automatically compiles and creates a default account with basic credentials. It is always good practice to use strong passwords for everything, and database credentials are no exception.
.
Say yes to the rest of the questions and use good judgement if it asks something that requires anything other than a Y/N input.
Installing PHP
Again, installing PHP is very similar to two sections preceding this one. Start off by installing the php-fpm and php-mysql packages by running sudo apt-get install php-fpm php-mysql. After it installs, you'll want to edit php.ini by running sudo vim /etc/php/7.2/fpm/php.ini.
.
Note: If the file isn't found, check the directory path by using the cd command and seeing where something doesn't exist.
.
If you're using Vim, type a ? and search for cgi.fix_pathinfo. You should be taken to a line that's commented out and says ;cgi.fix_pathinfo=0 or something similar. Press the i key to start editing and remove the ; to uncomment it. If the variable is set to 1, change it to 0. Press the escape key and type :wq to save and quit your changes. If you didn't run Vim as a superuser (if you didn't run the command with sudo), it will throw and error and the file won't save.
.
Once the file saves, run sudo systemctl restart php7.2-fpm to restart PHP.
Configuring nginx
The configuration for nginx is a little different compared to anything you might be used to. To start, there are two directories: sites-available and sites-enabled. The former directory actually contains the configuration files, while the latter contains symbolic links to the configuration files and enables them.
.
To start, lets say that we wanted to configure our nginx server to work with the domain example.ms. Move to the sites-available directory by entering the command cd /etc/nginx/sites-available. Next, you'll want to create a new configuration file with the name of the domain. You can either by running sudo touch example.ms && sudo vim example.ms or simply by running sudo vim example.ms since Vim creates the file if it doesn't exist. Again, press i to edit the file. Once you're in edit mode, you'll want the contents to look something like this:
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name example.ms;
root /var/www/example.ms;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
location = /favicon.io {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php$args;
}
location ~\.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
}
location ~* \.(js|css|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|ico)$ {
expires max;
log_not_found off;
}
}
Tip: You can periodically save your configuration file by pressing escape, typing :w , and then pressing i again to edit the file.
.
Once you're completely done editing, save and quit the file by pressing the escape key and typing :wq. Finally, you can check your configuration file for errors by running sudo nginx -t. If there are any errors, refer back to your configuration file and see where you went wrong. In the event that nginx threw an error, review your configuration file and look for any missing {, }, or ;. Every line that doesn't have curly brackets should end in a semicolon, which is probably the issue. If that isn't, then refer to your favorite search engine and start researching.
.
If nothing went wrong, and your configuration file is completely free of errors, run cd ../sites-enabled to move to the sites-enabled directory