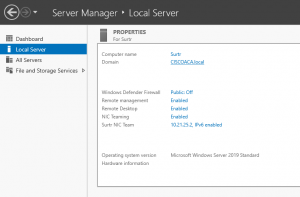
NIC Teaming
Introduction
NIC Teaming is using two or more Ethernet ports simultaneously in a team as a ambiguate. An ambiguate is a sort of situation in which something is getting labeled as ambiguous, a NIC Team is making the wired connection to the internet ambiguous for security reasons. This is very useful for servers where constant web services are required, just in case one fails another one is already set up.
Creating or Editing a NIC Team
In Windows Server open the “Server Manager” window and navigate to the “Local Server” category. Look for the “NIC Teaming” option and it will either say “Disabled” or “Enabled” click on this to open the “NIC Teaming” window.
Editing
Click on an existing NIC Team and edit the options to fit your needs, see Options and What to Use heading.
Creating a New Team
Click on the “Tasks” drop-down menu next to the Teams category. Select the “New Team” option, this will open a new window. The available Ethernet Adapters will be shown on the bottom left corner. Make sure all of them are connected to a router and have connectivity.
Select the Ethernet Adapters you would like to use, make sure you select two or more for an effective NIC Team. Once selected give the team an appropriate name and then select the appropriate options for the team under the Additional Properties tab. See Options and What to Use for help on these options. Once all are set, press “OK” and verify connectivity.
Verifying Connectivity
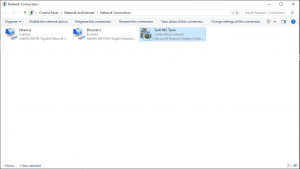
Navigate to Control Panel, Then click on “Network and Internet”, then “Networking and Sharing Center”, then next to Connections click on “Ethernet” or Hopefully the name assigned to your NIC Team will show up. If the name of your NIC Team shows up then connectivity is established. If not click on it and a “Properties” window should pop up. Use this window to verify connectivity, if not plausible do basic networking troubleshooting for the NIC Team.
Options and What to Use
Teaming Mode
Two available options, Switch Dependent and Switch Independent.
With Switch Independent mode, the switch or switches to which the NIC Team members are connected are unaware of the presence of the NIC team and do not determine how to distribute network traffic to NIC Team members - instead, the NIC Team distributes inbound network traffic across the NIC Team members.
With Switch Dependent modes, the switch to which the NIC Team members are connected determines how to distribute the inbound network traffic among the NIC Team members. The switch has complete independence to determine how to distribute the network traffic across the NIC Team members.
Load Balancing Mode
Three Available options, Address Hash, Hyper-V Port, and Dynamic.
With Address Hash, this mode creates a hash based on address components of the packet, which then get assigned to one of the available adapters. Usually, this mechanism alone is sufficient to create a reasonable balance across the available adapters. The TCP ports hash creates the most granular distribution of traffic streams, resulting in smaller streams that can be independently moved between NIC team members. However, you cannot use the TCP ports hash for traffic that is not TCP or UDP-based, or where the TCP and UDP ports are hidden from the stack, such as with IPsec-protected traffic. In these cases, the hash automatically uses the IP address hash or, if the traffic is not IP traffic, the MAC address hash is used.
With Hyper-V Port, NIC Teams configured on Hyper-V hosts give VMs independent MAC addresses. The VMs MAC address or the VM ported connected to the Hyper-V switch, can be used to divide network traffic between NIC Team members. You cannot configure NIC Teams that you create within VMs with the Hyper-V Port load balancing mode. Instead, use the Address Hash mode. Because the adjacent switch always sees a particular MAC address on one port, the switch distributes the ingress load (the traffic from the switch to the host) on multiple links based on the destination MAC (VM MAC) address. This is particularly useful when Virtual Machine Queues (VMQs) are used because a queue can be placed on the specific NIC where the traffic is expected to arrive. However, if the host has only a few VMs, this mode might not be granular enough to achieve a well-balanced distribution. This mode will also always limit a single VM (i.e., the traffic from a single switch port) to the bandwidth that is available on a single interface. NIC Teaming uses the Hyper-V Virtual Switch Port as the identifier instead of using the source MAC address because, in some instances, a VM might be configured with more than one MAC address on a switch port.
With Dynamic, outbound loads are distributed based on a hash of the TCP ports and IP addresses. Dynamic mode also rebalances loads in real-time so that a given outbound flow may move back and forth between team members. Inbound loads, on the other hand, get distributed the same way as Hyper-V Port. In a nutshell, Dynamic mode utilizes the best aspects of both Address Hash and Hyper-V Port and is the highest performing load balancing mode. When you use Switch Independent mode with Dynamic distribution, the network traffic load is distributed based on the TCP Ports address hash as modified by the Dynamic load balancing algorithm. The Dynamic load balancing algorithm redistributes flows to optimize team member bandwidth utilization so that individual flow transmissions can move from one active team member to another. The algorithm takes into account the small possibility that redistributing traffic could cause out-of-order delivery of packets, so it takes steps to minimize that possibility.
Standby Adapter
None or a certain selection based on the NIC Adapters selected.
Just simply select a standby(s) and then proceed with the rest of the Options. No standby has to selected, but it is recommended if you have extra Ethernet Adapters available.
If you have a two-NIC team and you choose to configure one NIC as a Standby adapter, you lose the bandwidth aggregation advantages that exist with two active NICs. You do not need to designate a Standby Adapter to achieve fault tolerance; fault tolerance is always present whenever there are at least two network adapters in a NIC Team.
Primary Team Interface
The options are a Default setting, or either a Custom VLAN.
If you are using a VLAN then select Custom VLAN and input the VLAN number.
Citations
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/networking/technologies/nic-teaming/nic-teaming